An overview of sickle cell anemia
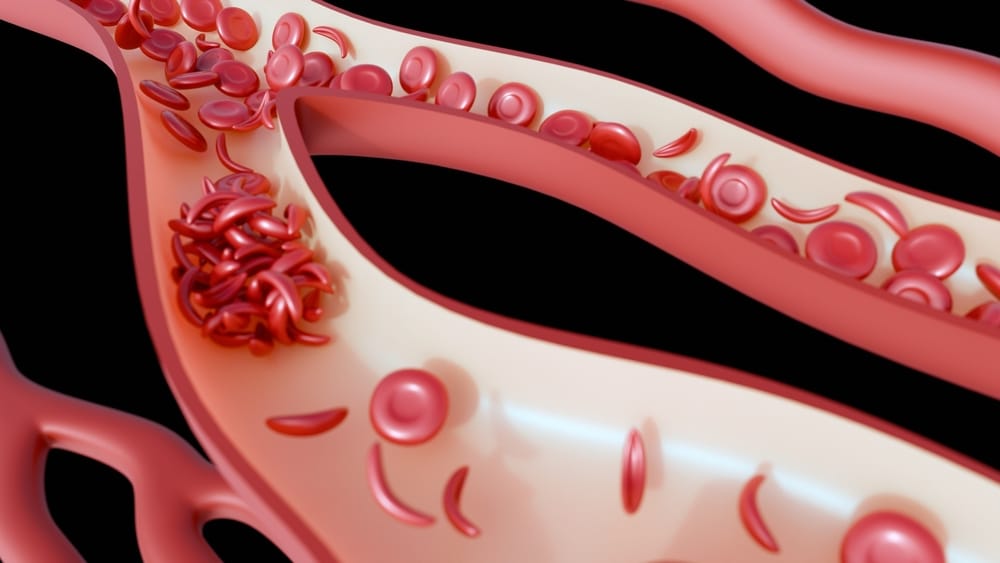
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder that affects over 20 million people worldwide. It is caused by mutations in both copies of the hemoglobin gene, leading red blood cells to take on a distinctive crescent or sickle shape instead of the normal round form. These misshapen cells are less flexible and have a much shorter lifespan (10 to 20 days compared with the 120 days of normal red blood cells) which disrupts blood flow and reduces oxygen delivery to organs.
Interestingly, individuals who inherit a mutation in only one hemoglobin gene are considered heterozygous. These carriers often do not experience symptoms of the disease and gain a survival advantage against malaria, a mosquito-borne infection.
The reduced oxygen transport in sickle cell anemia can trigger painful episodes called pain crises, which may vary in severity, duration, and location throughout the body. Over time, repeated crises and poor blood flow can cause serious complications, including stroke, pulmonary hypertension, blindness, and acute chest syndrome. These complications make the disease potentially life-threatening, contributing to an average life expectancy of around 50 years for affected individuals.
Currently, the only approved curative treatment is a bone marrow or stem cell transplant. While this approach can be effective, it carries significant risks, including severe complications and even death, limiting its availability and suitability for many patients.
Management of sickle cell anemia also focuses on symptom relief, preventing crises, and monitoring for complications. Approaches may include pain management, hydration, and medications to reduce sickling of red blood cells.
The Boom Health app allows users to book registered nurses, personal support workers, and personal care services, schedule transportation, order prepared meals, rent or purchase medical equipment, and get emergency assistance. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.