Hypertension in seniors: what you need to know
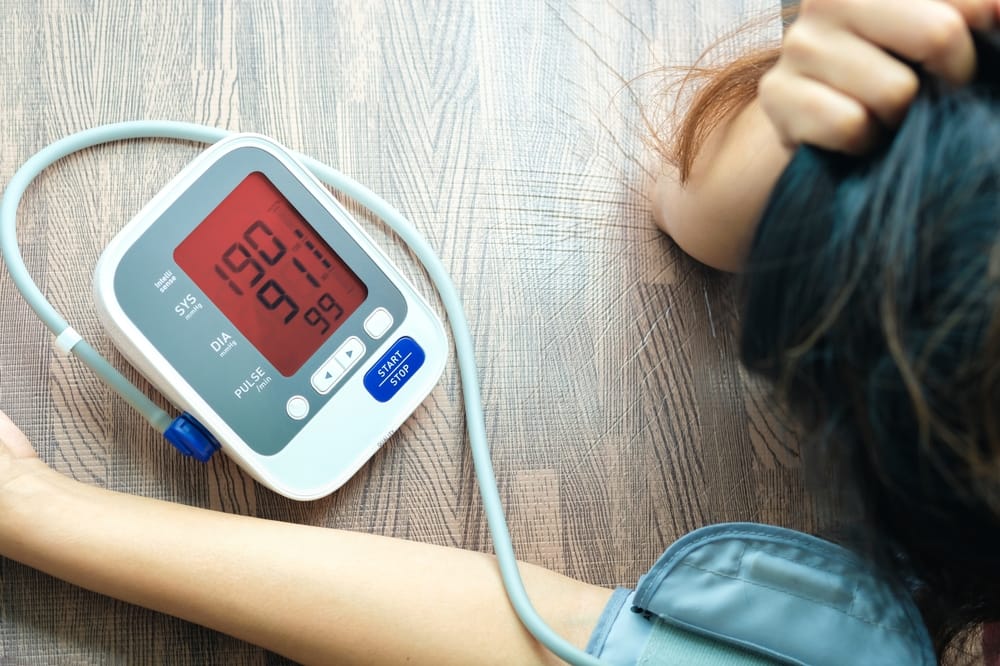
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs when the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure varies during the cardiac cycle, which has two main phases: systole and diastole. Systole is when the heart contracts to pump blood out, while diastole is the relaxation phase when the heart fills with blood. Blood pressure is measured with two numbers—systolic over diastolic—and is considered normal when it is below 120/80 mmHg. Prehypertension is diagnosed when systolic pressure ranges from 120 to 139 mmHg or diastolic pressure from 80 to 89 mmHg. Stage 1 hypertension is defined by a systolic reading of 140–159 mmHg or diastolic of 90–99 mmHg, and stage 2 hypertension is marked by a systolic pressure over 160 mmHg or diastolic over 100 mmHg.
Approximately 92% of hypertension cases are classified as primary hypertension, meaning there is no identifiable cause. The remaining cases are known as secondary hypertension and are linked to underlying conditions such as kidney disease, hyperthyroidism, pregnancy, sleep apnea, or the use of certain medications like oral contraceptives. Several factors can affect blood pressure levels, including the amount of water and salt in the body, kidney function, the health of the nervous system and blood vessels, and the balance of hormones. Additionally, risk factors such as obesity, smoking, chronic stress, high salt intake, and diabetes increase the likelihood of developing hypertension.
Chronic hypertension can significantly increase the risk of serious health complications, including heart attacks, strokes, kidney failure, and damage to the eyes. The good news is that lifestyle changes can effectively manage or even prevent high blood pressure. Key strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, reducing sodium intake, staying physically active, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
Love them without losing yourself. The Boom Health app helps you manage your loved one’s home care in one app. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.