Understanding the basics of inflammation
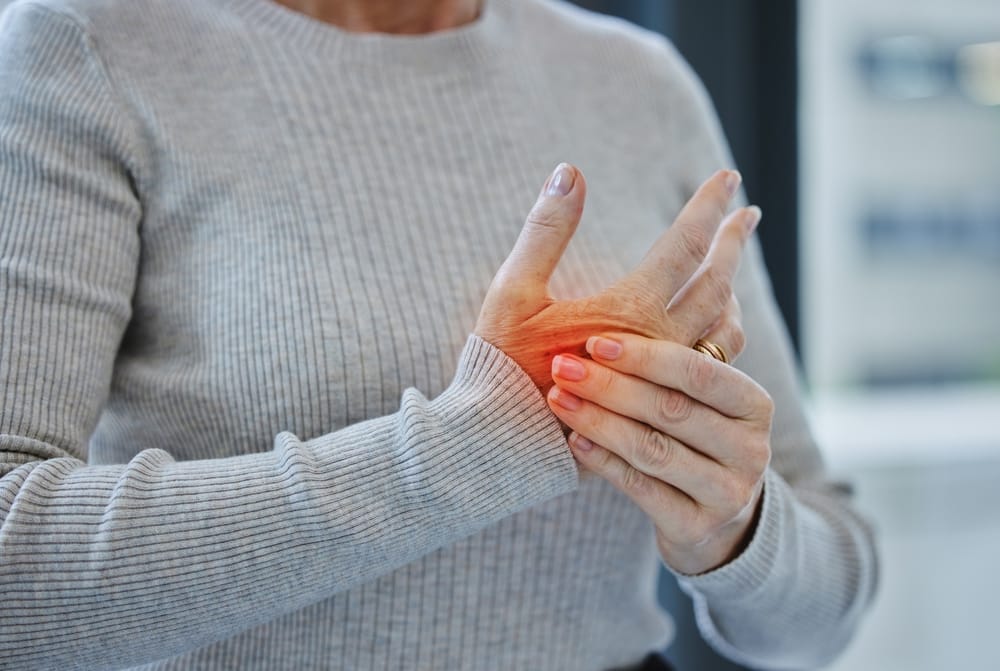
Inflammation is the body’s natural response in tissues with blood vessels, where immune cells and defense molecules are sent from the bloodstream to areas affected by infection or injury. This process helps eliminate harmful agents and promotes healing.
Inflammation can be categorized as either acute or chronic based on its duration. Acute inflammation usually lasts for a few hours to days and may cause symptoms like pain, tenderness, warmth, and swelling. On the other hand, chronic inflammation can persist for months or even years, often presenting with symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and skin rashes.
Chronic inflammation is linked to several neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Huntington’s disease. Additionally, many forms of arthritis—such as gouty arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis—are driven by inflammatory processes.
The inflammatory response starts when damaged tissue cells release chemical signals that activate the inner lining of nearby capillaries. Mast cells then release histamine, which widens blood vessels and allows neutrophils to move into the tissue. These neutrophils then engulf and destroy invading bacteria to protect the body.
To help prevent inflammation, it is advisable to limit alcohol intake, stay physically active, maintain a healthy weight, and avoid smoking. When inflammation occurs, treatments may include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroid injections, and dietary supplements. Besides reducing inflammation, NSAIDs also help prevent blood clots, lower fever, and alleviate pain.
The Boom Health app allows users to book registered nurses, personal support workers, and personal care services, schedule transportation, order prepared meals, rent or purchase medical equipment, and get emergency assistance. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.