Understanding the respiratory system
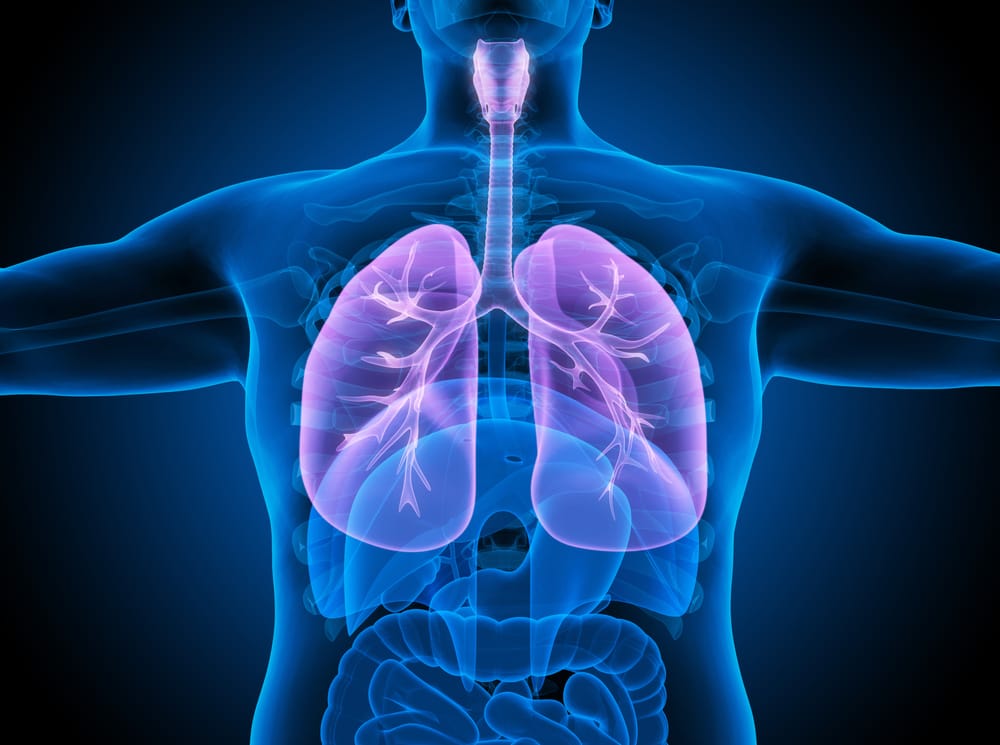
The respiratory system plays a vital role in sustaining life by facilitating the intake of oxygen and the removal of waste gases, primarily carbon dioxide, from the body. This continuous exchange is essential for cellular function and overall health.
Anatomically, the respiratory system is divided into two main parts: the conducting portion and the respiratory portion. The conducting portion acts as a passageway that transports air into the lungs. Its primary functions include conducting air, filtering out harmful particles, humidifying the air to protect delicate lung tissues, and warming it to body temperature. This section begins at the nasal cavity and extends through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and ends at the terminal bronchioles.
Beyond the conducting portion lies the respiratory portion, where the critical process of gas exchange takes place. This area starts at the respiratory bronchioles and includes the alveoli—tiny, balloon-like sacs where oxygen passes into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed. The alveoli’s thin walls and vast surface area make them perfectly suited for efficient gas exchange.
Within the respiratory system, specialized immune cells known as alveolar macrophages play a key protective role. These cells engulf and digest inhaled particles, bacteria, and other antigens, helping to keep the lungs clean and free from infection. Alveolar macrophages are transported upwards along the bronchial tree within mucus, propelled by the coordinated beating of cilia. Eventually, these trapped particles are cleared from the respiratory tract through swallowing or coughing.
Another critical component of lung health is surfactant, a substance produced by cells within the lungs. Surfactant reduces surface tension in the alveoli, preventing them from collapsing after each breath and ensuring the lungs remain open and functional during respiration.
As we age, natural changes occur in the respiratory system, including a gradual decrease in lung capacity and efficiency. Despite these changes, maintaining respiratory health is possible through proactive measures. Preventing respiratory infections, avoiding smoking, consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients, and engaging in regular physical activity can all contribute to preserving lung function and overall well-being throughout life.
Love them without losing yourself. The Boom Health app helps you manage your loved one’s home care in one app. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.