Understanding the science behind hearing
Audition is the sense responsible for hearing and the perception of sound. As people age, hearing often gradually declines, a condition known as presbycusis. This age-related hearing loss occurs due to changes in the inner ear that affect its ability to transmit sound signals to the brain. Hearing depends on both pressurized sound waves and healthy auditory hair cells that convert these waves into neural signals.
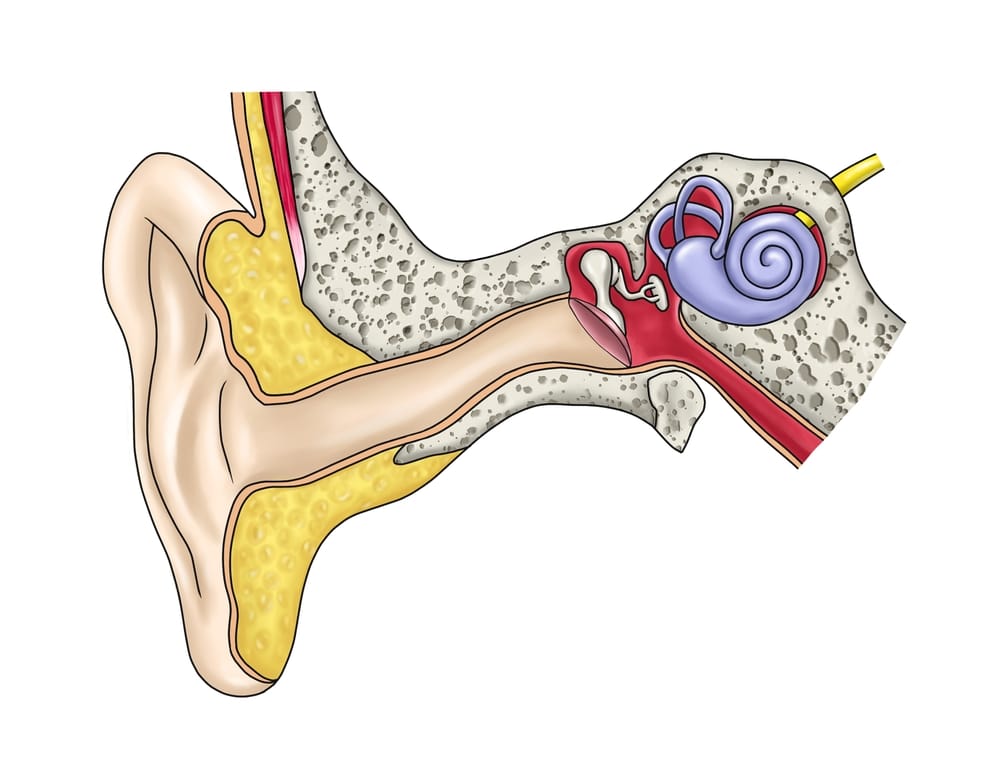
The ear is divided into three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear includes the pinna, auditory canal, and tympanic membrane (eardrum). The middle ear contains three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes, collectively known as the ossicles. The inner ear consists of the cochlea and the semicircular canals.
The hearing process begins when sound waves are collected by the pinna and funneled through the auditory canal to the tympanic membrane. When the eardrum vibrates, it causes the ossicles, the three smallest bones in the human body, to move back and forth, amplifying the sound.
The stapes connects to the oval window, a membrane-covered opening that leads into the cochlea. Vibrations at the oval window create fluid movement within the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure lined with specialized auditory hair cells. As these hair cells bend in response to fluid movement, they convert mechanical vibrations into electrical impulses, which are then transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
According to the place theory of hearing, the perception of sound pitch depends on where vibrations occur within the cochlea. Different sound frequencies stimulate different regions of the cochlea, allowing the brain to distinguish between high- and low-pitched sounds.
Love them without losing yourself. The Boom Health app helps you manage your loved one’s home care in one app. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.




