Understanding the urinary system
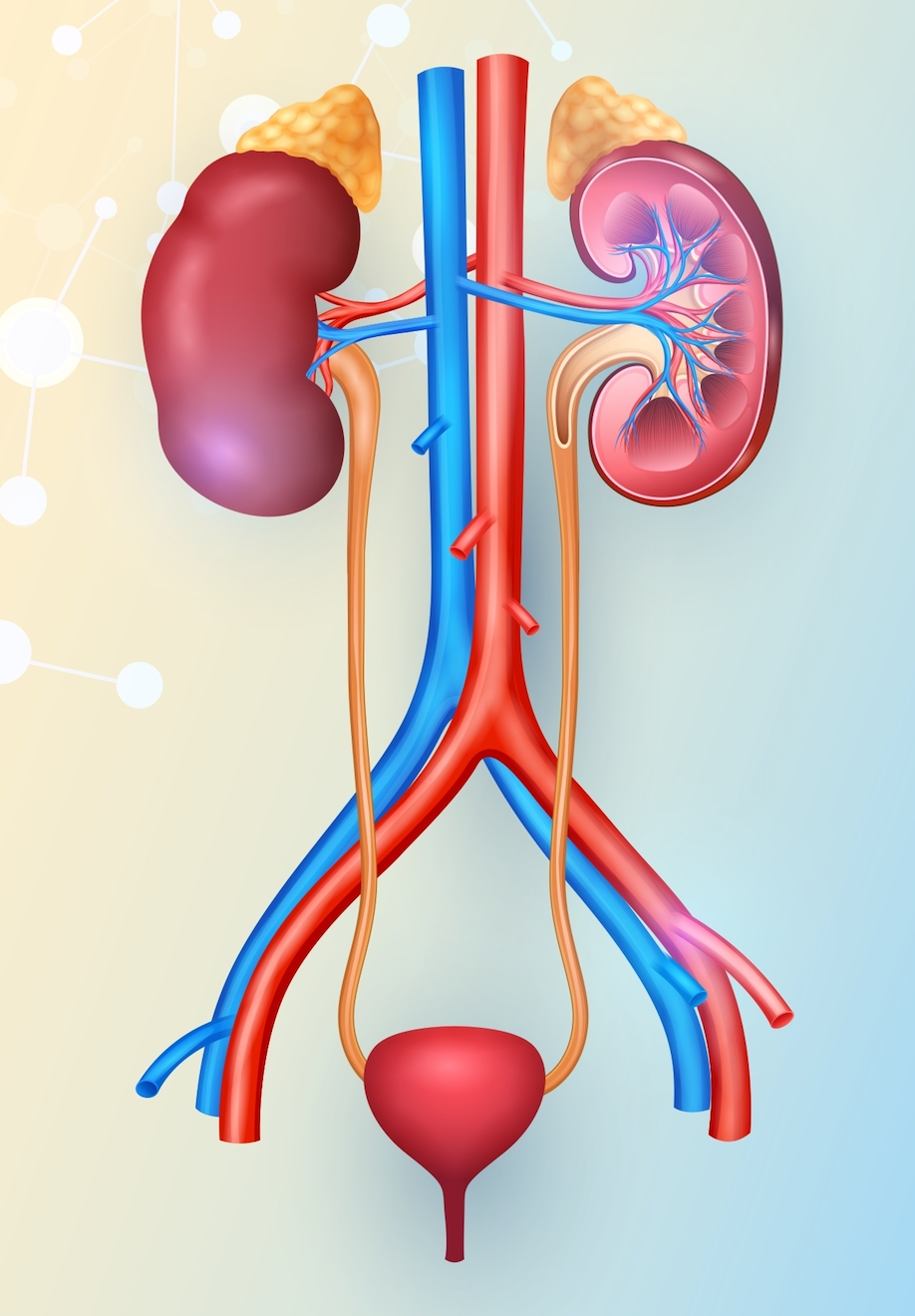
The urinary system is one of the body’s most important cleansing systems. Every day, it works to filter blood, remove waste products, and keep water, electrolytes, and nutrients in balance. While often overlooked, it plays a central role in maintaining overall health.
The system is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, each with a unique function.
The kidneys are the body’s main filters. Located just below the ribcage, these bean-shaped organs filter nearly 200 liters of blood daily. They reabsorb vital substances such as glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and electrolytes, while excess water and waste are excreted as urine. Each kidney contains about a million filtering units, called nephrons, though their number and efficiency decrease with age. This natural decline explains why kidney function weakens over time, making older adults more vulnerable to dehydration and kidney disease.
Urine then travels through the ureters, narrow muscular tubes lined with transitional epithelium, which allows them to stretch as liquid moves from the kidneys to the bladder.
The bladder acts as a storage reservoir, typically holding 1.5 to 2 cups of urine. Its elastic walls expand to accommodate increasing volume. With age, however, bladder tissue loses elasticity, reducing its capacity and leading to more frequent urination.
Finally, urine exits through the urethra. In men, the passage may become obstructed by an enlarged prostate gland, while in women, weakened pelvic muscles can cause the bladder or vagina to shift out of place, disrupting normal flow.
Beyond waste removal, the urinary system regulates blood pressure, red blood cell production, and acid-base balance. Keeping it healthy, through hydration, diet, and regular checkups, is essential for long-term well-being.
The Boom Health app allows users to book registered nurses, personal support workers, and personal care services, schedule transportation, order prepared meals, rent or purchase medical equipment, and get emergency assistance. Download the app from the App Store or Google Play Store.
This article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice or diagnosis. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.